The Physics of Physiology - Example 1: An electrical circuit
Bond graph example: An electrical circuit
Here we show an electrical circuit with static storage (capacitor C), dynamic storage (inductor L) and dissipation (resistor R). vein and veout are the input and output fluxes (electrical currents), respectively. veC, veR and veL are the currents flowing through capacitor C, resistor R and inductor L, respectively, and ueC, ueR and ueL are the electrical potentials across them. Superscript ‘e’ indicates that the variables are electrical quantities; subscripts indicate the location in the circuit for each quantity.
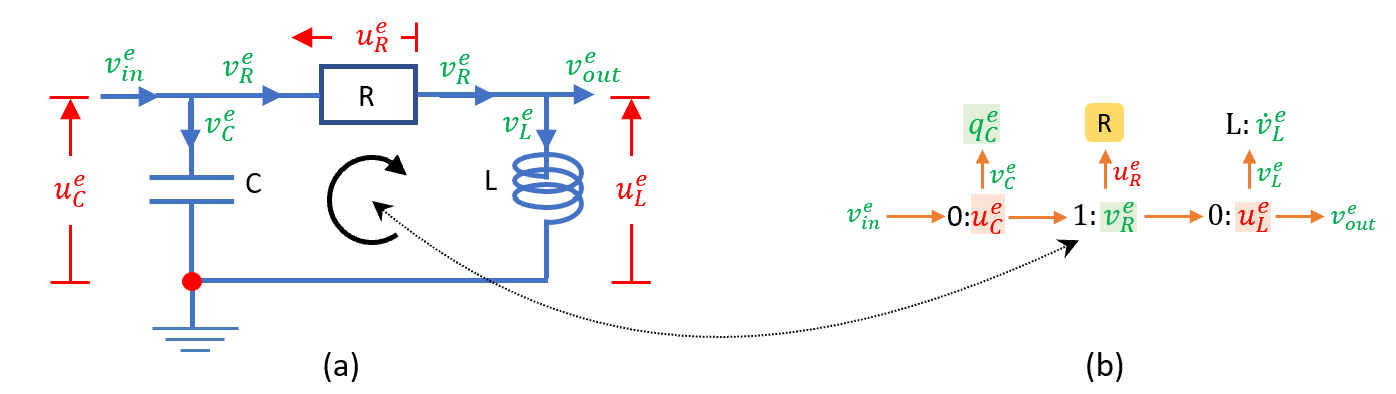
A simple electrical circuit (a) with its representation by a bond graph (b). 0:nodes for an electrical network are physical locations where the flows (electrical currents) are balanced, while 1:nodes represent circuits around which the potentials sum to zero. vein and veout are boundary conditions.
There are two implementations of this model available:
- The standard BG model from the lecture notes: FAIRDO BG example 3.1; and
- A version with the full power and energy calculations shown: FAIRDO BG example 3.1.1
