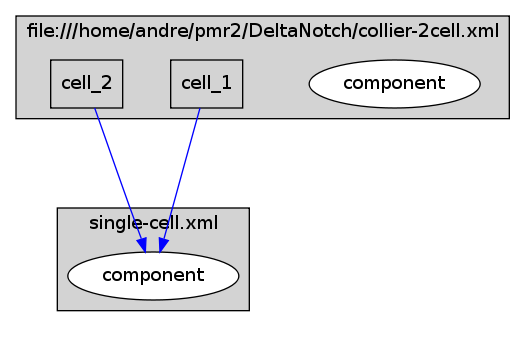
Model hierarchy (generated using CellML2Dot) of the two cell variant of the Collier et al Delta-Notch signalling model.
An initial attempt to demonstrate one use of CellML with multicellular models using the Delta-Notch model of Collier et al (1996) as an example. In the current state of this workspace, I show the two cell variant of the Collier model as described in Figure 3 of the Collier article. In this encoding of the model, we use CellML 1.1 to separate the single cell dynamics from the population model. In the single cell model I have encoded the two ODEs which make up the dynamics (Equation 2 in the Collier paper) and left the initial conditions and parameters undefined. The population model (collier-2cell.xml) uses the CellML import feature to "instantiate" two cells, as shown in the diagram below:

The two single cell models are then connected together in the two cell variant of the Collier model. The parent model defines the parameters to be used in both instances of the single cell model along with the different initial conditions for each cell. I define a neighbourhood average for delta for each of the cells, which for the two cell variant simply consists of the delta value from the other cell and the zero boundary condition. The connections between the single cell models can be seen in the figure below:

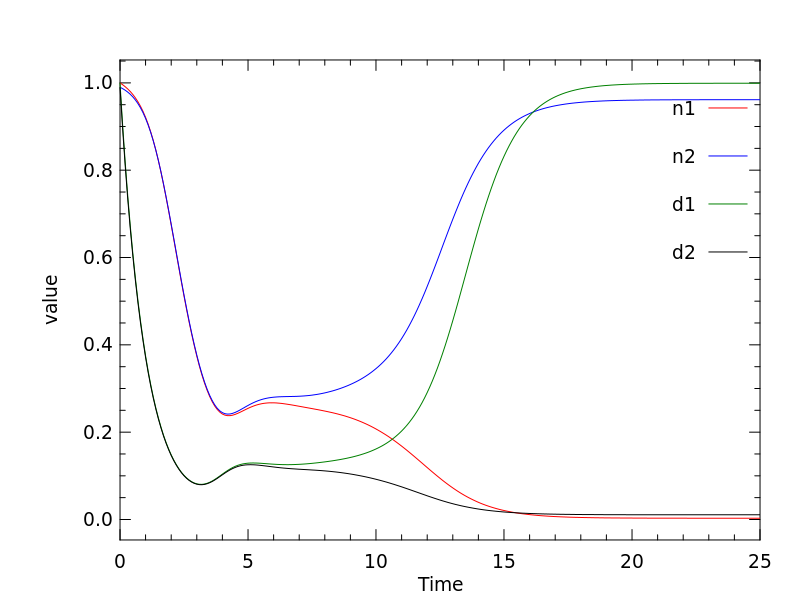
Simulations of the two cell variant of the Collier model can be performed to demonstrate that the model is correctly encoded. A reproduction of the results from Figure 3 of the Collier et al (1996) article can be seen below, using the two cell variant as encoded in CellML.