CaL protein knowledge page
About
Landing page for the L-type calcium pump CaL.
CaL allows for calcium entry into the cell and is responsible for triggering muscle contraction predominantly within cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscle cells.
When the cell membrane is depolarised above a given potential (such as during an action potential) the gated, voltage-dependent channel opens to allow for calcium entry.
CaLs are multisubunit complexes, consisting of a combination of alpha, beta, gamma and delta subunits. The channel activity is generally directed by the pore-forming and voltage-sensitive alpha subunit.
Other names: Cav1, LCC
Pictures
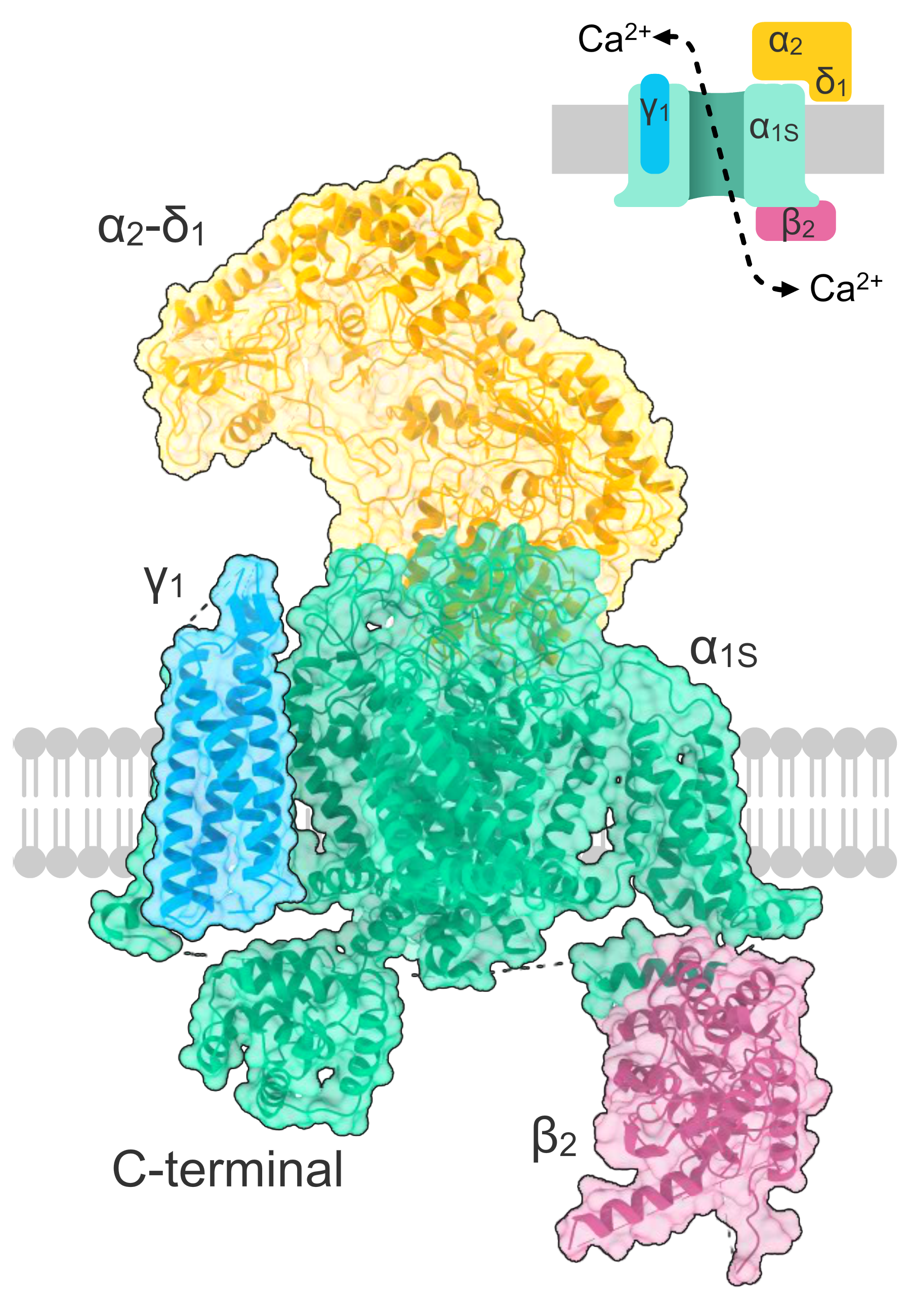
Fig 1: Crystallographic structure of the L-type calcium channel complex.
Subfamilies
The following list contains all known isoforms of the L-type voltage dependent calcium channel family. Only the pore-forming alpha subunits are included.
| Name | Alias | Gene | Structure | Modulated by |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CACNA1C | Cav1.2 | Uniprot C | PDB C | CACNB1/CACNB2/CACNB3/CACNA2D1/CACNA2D4/CACNG4/CACNG6/CACNG7/CACNG8 |
| CACNA1D | Cav1.3 | Uniprot D | PDB D | CABP1/CABP4 |
| CACNA1F | Cav1.4 | Uniprot F | Alphafold F | CABP4 |
| CACNA1S | Cav1.1 | Uniprot S | PDB S | CACNB1/CACNB2/CACNG1/CACNA2D1 |
Literature
| Title | Author |
|---|---|
| L-Type Calcium Channels: The Low Down | Lipscombe et al. |
| A thermodynamic framework for modelling membrane transporters | Pan et al. |
Existing models
| Title | Author |
|---|---|
| BG_LCC | S Fong |
| Bond graph modelling of the cardiac action potential: Implications for drift and non-unique steady states^ | M Pan et al. |
| IPSC-model | Kernik et al. |
Models denoted by [*] are not in bond graph form. Models denoted by [^] are part of a whole cell model.
Other annotations
| Item | Database |
|---|---|
| voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential | Gene Ontology |
