CaT protein knowledge page
About
Landing page for the T-type calcium pump CaT.
CaT allows for calcium entry into the cell and is responsible for hekping trigger muscle contraction predominantly within cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscle cells. T-type calcium channels belong to the 'low-voltage activated (LVA)' group. Normally closed, this type of channel iopens at quite negative potentials and has voltage-dependent inactivation, the latter achieved during cell hyperpolarisation. Gating of this channel is also voltage-dependent.
CaT are made of a primary alpha subunit that forms the pore. As in other calcium channels, there may also be beta, gamma, and delta auxiliary subunits that are involved in channel regulation, but are likely absent from CaT.
Other names: Cav3, TCC
Pictures
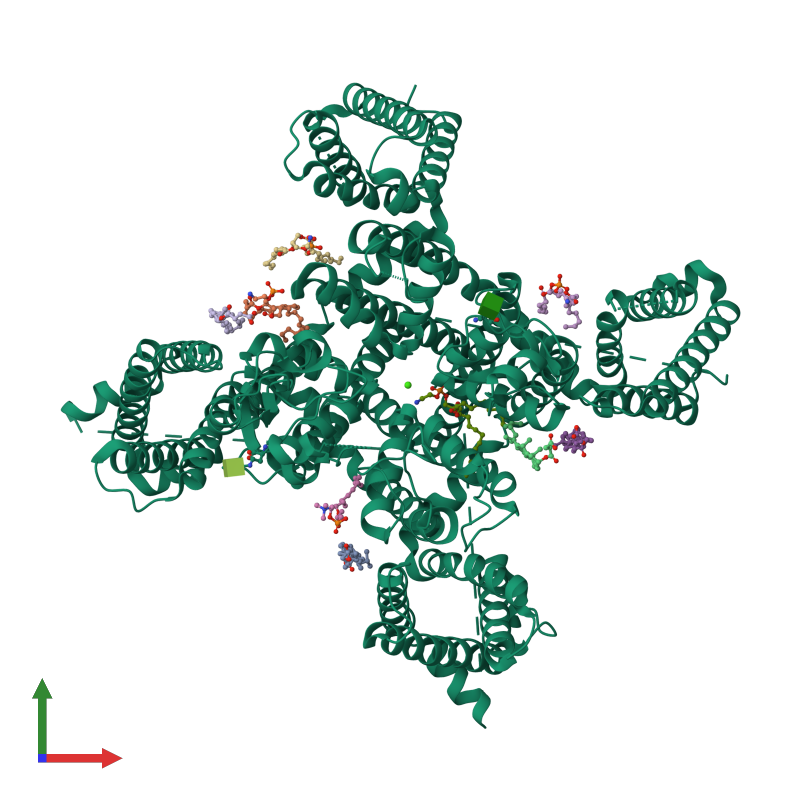
Fig 1: PDB image of CACNA1H from https://dx.doi.org/10.2210/pdb9ayg/pdb
Subfamilies
The following list contains all known isoforms of the T-type voltage dependent calcium channel family.
| Name | Alias | Gene | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| CACNA1G | Cav3.1 | Uniprot G | PDB G |
| CACNA1H | Cav3.2 | Uniprot H | PDB H |
| CACNA1I | Cav3.3 | Uniprot I | PDB I |
Literature
| Title | Author |
|---|---|
| T-type calcium channels: From molecule to therapeutic opportunities | Weiss and Zamponi |
Existing models
| Title | Author |
|---|---|
| BG_TCC | S Fong |
| IPSC-model | Kernik et al. |
Models denoted by [*] are not in bond graph form. Models denoted by [^] are part of a whole cell model.
Other annotations
| Item | Database |
|---|---|
| voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential | Gene Ontology |
